Generator load bank testing: the basics
- BY BISON
Table of Contents
In critical environments like hospitals, data centers, and emergency facilities, power outages are not only inconvenient, they can also be dangerous and costly. Power availability can be a matter of life and death for those in the healthcare industry. For those operating data centers or working in the financial industry, a catastrophic power outage can cost millions or tens of millions of dollars in lost revenue. Therefore, generators must always be up and running when needed. Generators that act as backup power systems should automatically provide power when the main power source is lost, keeping important systems running smoothly.
To ensure that these backup generators are always available, this article will introduce you to a comprehensive guide to generator load bank testing. This test simulates real power loads to help identify potential problems with the generator, such as fuel problems, cooling system failures, and electrical anomalies. It’s like running a test run of the generator under real conditions to ensure that it performs as expected.

What is generator load bank testing and why is it important?
What is a load bank?
A load bank is a device used to test generators by applying a simulated electrical load, mimicking the kind of power the generator would need to supply during real-life use. During a load bank test, an artificial load is placed on the generator, gradually increasing the kilowatt load (usually in the form of resistance or reactance) in specific increments. Each time the load increases, engine and alternator parameters are recorded to monitor performance under full load.
What is generator load bank testing?
A generator load bank test involves testing and diagnosing a genset to verify that all of the generator set’s core components are in proper working condition to operate under heavy load conditions. The equipment used to perform a load bank test creates an artificial load on the generator by bringing the engine to the proper operating temperature and pressure. The general rule is: that if your generator does not experience more than 30% of its rated kW load, you should consider a load bank test.
Testing your generator at its maximum kilowatt (kW) output rating is essential to ensure it operates properly when required. Since many generators do not normally run at their full kilowatt rating, you need to make sure your generator can generate the maximum horsepower needed while maintaining the proper temperature and pressure levels to run for as long as necessary.
Benefits of load bank testing
- Ensuring proper functioning: The test confirms that the generator can handle the power it will need to produce in real situations. Verifying the generator’s capabilities beyond routine starts.
- Preventing problems like wet stacking: If a diesel engine-powered generator is not used frequently or only runs at low loads, it may accumulate unburned fuel and soot in the exhaust system, leading to wet stacking. A load bank test helps avoid this by ensuring that the generator is running at maximum power and temperature, burning out any wet buildup.
- Maintaining generator reliability: Regular testing helps keep the generator in peak condition, reducing the risk of failure during emergencies. Identifying problems early to prevent costly major issues.
- Following regulations and standards: Many industries and safety standards require regular load testing to ensure generators are compliant with reliability and safety guidelines.
Preparing for a load bank test
Safety checks
- Wear protective gear: Wear devices such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection.
- Inspect the site: Make sure the test area is clean, dry, ventilated, and free of any hazards.
- Verify electrical connections: Double-check that all electrical connections are secure and that the generator is properly isolated from the mains if necessary.
Inspect the equipment
- Check the generator: Ensure the generator has been properly maintained, including oil levels, coolant, and fuel, to confirm it’s in good working condition before the test. If the generator is water-cooled, verify that the coolant tank or radiator is in good condition.
- Inspect the load bank: Verify that the load bank is in good condition and has no signs of wear or damage. Check cables, switches, and the cooling system to ensure they function properly.
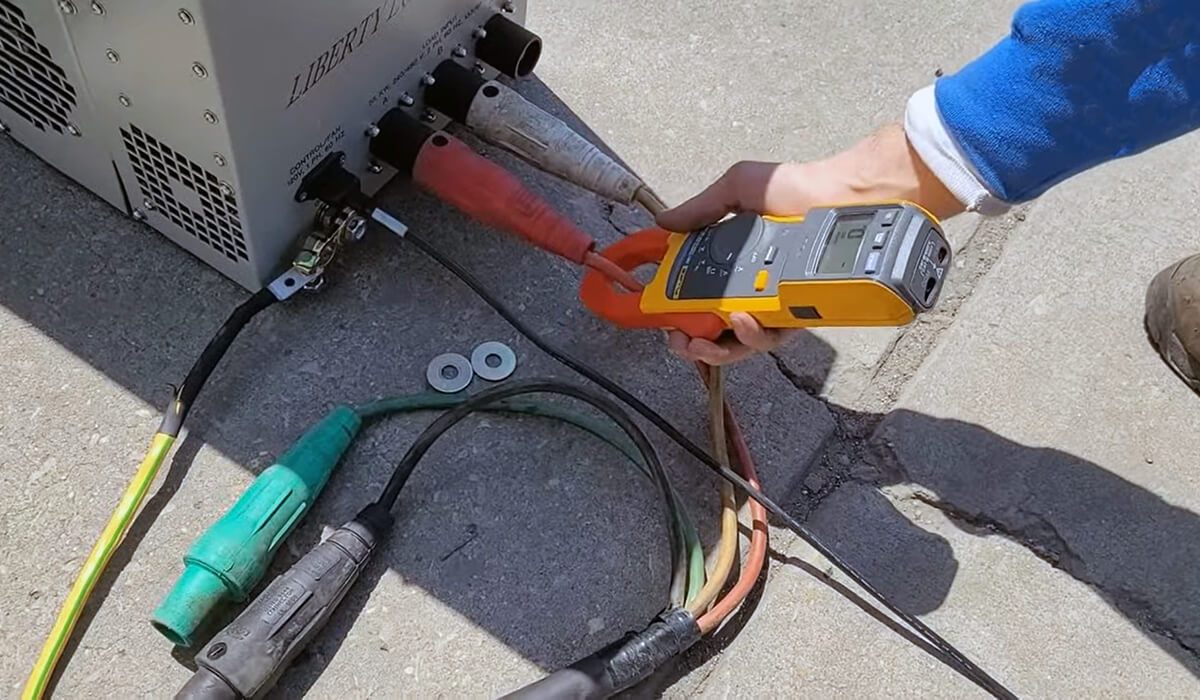

Create a test plan
- Determine the length of the test: Typically, load bank tests can last anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the size of the generator and the load requirements.
- Set the load level: Simulate typical operating conditions for the generator through expected usage or industry standards.
- Test objectives: Identify the specific goals of the test, such as checking fuel consumption, exhaust output, or ensuring that all components function properly under load.
Conducting the load bank test
Connect the load bank to the generator
- First, connect the load bank to the generator using the appropriate cables. Make sure the connections are secure to avoid electrical hazards. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the connection steps.
- The technician begins connecting the loads, starting with any large 200-volt loads and adding smaller 110-volt loads until each leg carries 50 percent of the current.
Begin the test
- Start the generator: Power on the generator and ensure it’s running smoothly before beginning the test. After starting, the generator is given time to reach its typical operating temperature.
- Gradually apply load: Begin adding load in stages, starting with a low load and gradually increasing it. This allows the generator to warm up and adjust before reaching full capacity. The technician uses an ammeter to measure each leg’s amperage. It is advised that the voltage on each leg drop between 105 and 125 volts when testing a 110/220-volt single-phase generator. For each leg, the current should be equal to half the rated wattage output divided by the voltage. A problem arises if one or more legs fall below 105 volts under full load, and the test is considered unsuccessful.
- Monitor performance: As the load is increased, carefully monitor the generator’s performance. Check for any unusual sounds, vibrations, or temperature increases. Pay attention to the output voltage and frequency to ensure they stay within acceptable ranges.
- Stabilize the load: Once the desired load is applied, allow it to stabilize for the specified test time, which may vary from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on factors such as the test schedule or the size of the generator.
The technician continues to monitor the generator for the duration of the test, maintaining the same load, listening for noise, and monitoring the output. If a problem is discovered, the test is shut down to minimize damage until repairs are made. After repairs, the test is restarted from the beginning.
Record the test results
- Monitor parameters: Track key performance indicators such as voltage, frequency, fuel consumption, and temperature.
- Record results: Record all readings during the test. Be sure to note any anomalies or problems that occur, such as excessive temperature rise, voltage fluctuations, or poor load handling.
End the test
- Gradually reduce the load: After the test, slowly remove the load and allow the generator to run at a light load for about an hour. This helps prevent sudden shocks to the system and ensures that the generator can smoothly return to idle.
- Shutdown and Inspection: Five to ten minutes before the generator shuts down, completely remove the load and shut down the load bank and generator. Review the test results to identify areas that require further attention or maintenance.
Conclusion
For industries where power loss can have serious consequences, regular load bank testing is critical. It prevents issues like wet stacking, ensures proper operation of cooling and electrical systems, helps reduce unexpected failures, improves performance, and extends the life of the generator. If you haven’t tested your generator recently, now is the time to schedule a load bank test.
If you are still looking for a generator, it is time to find a professional and cost-effective factory. Contact the trusted BISON generator manufacturing factory and get a batch of generators in the best condition and ready to respond to any emergency through BISON. We have the most complete and efficient after-sales system and customization process. Don’t worry about the quality and adaptation of the product. We only use first-class materials that have been tested, and we will arrange professional mechanical experts for you to make the most suitable generator model.
FAQs
Can load bank testing be performed on all types of generators?
Yes, the majority of generator types, including gas, diesel, and portable generators, can undergo load bank testing. The output and specifications of the generator will determine the size and kind of load bank needed.
What equipment is required for load bank testing?
The essential equipment required is a load bank, which can be resistive, inductive, or capacitive, depending on the test requirements. Additionally, temperature and power measurement instruments can be used to monitor the generator's performance.
Can load bank testing damage the generator?
When performed correctly, load bank testing should not damage the generator. It helps maintain the generator by ensuring that it is operating at full capacity and prevents carbon buildup in the engine. However, improper procedures or excessive loads can cause damage, so professional testing is recommended.
What Good Test Results Should Look Like
When performing a load bank test, good results are characterized by stable and normal operating conditions for the generator. Here’s what to look for:
- Voltage: The voltage output should remain steady and within the manufacturer's specifications.
- Frequency: The frequency should be kept at 50Hz or 60Hz, of course, depending on the standards in your area.
- Temperature: The generator should maintain an acceptable temperature range throughout the test. The engine and exhaust system must not overheat.
- Fuel consumption: A steady and predictable fuel consumption rate during the test is another sign of a healthy generator. Sudden spikes or irregular fuel usage could point to inefficiencies.
How often should load bank testing be performed on a generator?
For non-mission-critical generators, a load bank test is typically conducted once a year for 60 minutes at 80% of the maximum load. For generators in regular operation, testing is recommended after every 100 hours of use. However, the rating of the generator and its intended purpose can affect this schedule. For example, safety codes require more frequent testing for generators serving critical functions, such as backup power for hospitals or life-saving equipment.
If a monthly test fails, a two-hour load bank test is recommended.
contact us
related product categories
Get in touch to speak with our experts!




