How a generator transfer switch works: comprehensive guide
- BY BISON
Table of Contents
Generators provide crucial power during emergencies. They support hospital systems and keep businesses operational during outages.
However, the safe operation of generators requires a transfer switch. It ensures smooth power transfers and protects your equipment.
Next, BISON will explore generator transfer switches in this article. Read on to learn how they work, why they are vital, and more.

How does a generator transfer switch work?
A transfer switch connects a generator to a building safely. It lets backup power flow through circuits without using unsafe extension cords. This setup ensures reliable power and protects your system.
A transfer switch prevents dangerous backfeed. Backfeed happens when generator power flows to the grid, risking infrastructure. The transfer switch isolates home circuits, sending power only where needed.
Which generators require a transfer switch?
In most cases, the need for a transfer switch depends on the generator type, output. Let’s explore which generators require one.
Portable generators and standby generators
Portable generators:
A transfer switch is required if portable generator is designed to power multiple circuits in a home or building, such as appliances, lighting, or HVAC systems.
Standby generators:
Standby generators provide full-house power during outages. They connect to your electrical system with an automatic transfer switch. This switch ensures safe and instant power to multiple circuits.
Generators above a specific output
High output generators, whatever portable or standby, need a transfer switch. Not only for operational reasons, but also to comply with safety standards and electrical codes.
In summary, a transfer switch ensures safe, efficient, and legal operation. To protect your generator from avoidable risks.
Risks of not using a transfer switch on your generator
From electrical hazards to illegal actions, not using a transfer switch can have far-reaching consequences.
1. Electrical hazards
Generator misconnection creates serious electrical dangers, including electrocution and fire. A transfer switch is essential; without it, stray currents create unsafe conditions.
Also, improper isolation between generator and utility power can overload circuits. Overloads may lead to overheating and sparks, putting your property at risk of fire.
2. Damage to generators or appliances
Not using a transfer switch can also put your generator and home appliances at serious risk. Generators safely power specific circuits through controlled connections. Without a transfer switch, misrouted current can cause surges or overloads. These can damage appliances like refrigerators, HVAC systems or home computers.
Even generator itself is at risk. Improperly connecting a generator can cause performance problems. It may face mechanical failures from poor load management. This reduces its lifespan and lowers reliability during outages.
3. Legal and safety violations
Running a generator without a transfer switch can break safety codes. Many areas require proper installation to avoid risks like backfeed. Ignoring these rules may lead to fines, penalties or removal of your generator.
And skipping a transfer switch can void your generator’s warranty. Manufacturers require proper installation. Ignoring these rules may leave you unprotected if damage occurs.
4. Risks to utility workers
The biggest risk of skipping a transfer switch is worker safety. Utility workers face danger during power restoration. Backfeeding happens when your generator sends power into the grid without isolation.
Backfeeding sends power from your generator into utility lines. This creates a serious danger for line workers. They may unknowingly touch live wires. Workers expect de-energized lines during repairs. Backfeeding can cause electrocution or fatal accidents. A transfer switch stops current from flowing into the grid, and keeps utility crews safe during power restoration.
Transfer switches ensure proper power management and isolation. They protect your home and keep your generator reliable. They also safeguard everyone during emergency power situations.
Types of generator transfer switches
Transfer switches are mainly manual or automatic types.
Manual transfer switches
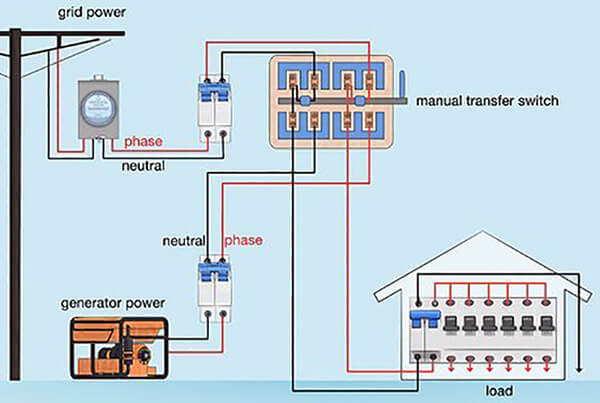
Manual transfer switches require physical engagement to shift power from the utility grid to a generator. Once power is restored, you must manually switch it back.
Pros
Affordable: Manual transfer switches cost less than automatic options, making them budget friendly.
Durable: With a simple design, these transfer switches are reliable for long-term use.
Cons
Manual operation required: You need to be present during outages, which can be inconvenient, especially in extreme conditions.
Not Ideal for Critical Uses: Delays in restoring power may affect essential systems.
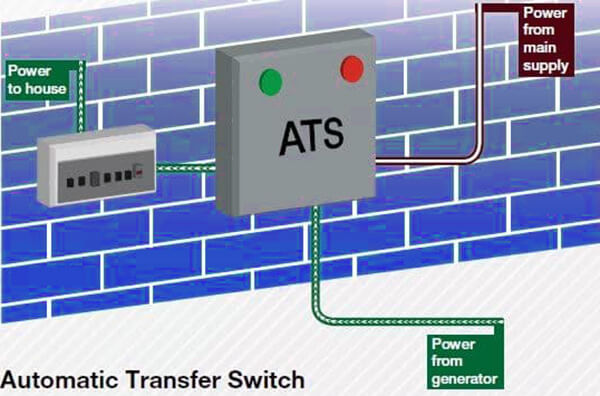
Automatic transfer switches (ATS)
An ATS handles power shifts seamlessly between the grid and generator without human input. It monitors power status and reacts as needed. Learn: How does ATS work with generators.
Advantages
Convenient: ATS automatically transfers power, ideal when you’re away or in emergencies.
Great for critical needs: Perfect for systems like medical devices, servers or HVAC, where downtime isn’t an option.
Disadvantages
Costly: ATS systems have higher upfront costs and may need more maintenance.
Complex installation: Professional expertise is necessary, increasing installation expenses.
Choosing the right transfer switch
Your choice depends on your needs, budget and convenience preferences. Manual transfer switches suit those seeking an affordable and simple solution. For uninterrupted power or critical systems, ATS offers reliability and peace of mind.
Generator transfer switch installation
Installing a generator transfer switch requires understanding the step-by-step process from selecting correct transfer switch to wiring the circuit, as well as following proper safety precautions and regulations, to ensure reliable backup power during a power outage without compromising safety or damaging equipment.
While DIY installation may seem appealing, having a professional install generator transfer switch is the safest option, compliance with local regulations and avoid costly mistakes.
At BISON, we’re here to help you with all of generator needs, including transfer switches. To determine the type you need and size that will work best for your specific situation. Contact BISON generator manufacturers today to learn more about generators and transfer switches.
contact us
related product categories
Get in touch to speak with our experts!




