wet stacking in diesel generators: causes and solutions
- BY BISON
Table of Contents
Diesel generator is essential to ensure stable power, especially in remote areas with power outages or no grid access. These durable devices transform diesel into electricity, maintaining operations when standard power sources are unavailable.
Diesel generators can face specific issues, including “wet stacking“. This happens when running the engine at ideal temperatures leads to unburned fuel building up in the exhaust system. Wet stacking can decrease efficiency, raise maintenance expenses, and potentially cause lasting harm to diesel generator.
In this piece, BISON explores the causes and effects of wet stacking, its impact on diesel generator performance, and offers practical solutions to lessen these effects. Gain a deeper understanding of wet stacking to improve maintenance and extend the life of diesel generators. Keep reading to find key tips and insights that help enhance diesel generator reliability while saving you time and money.

Causes of wet stacking in diesel generators
low load operation
Diesel generators running at low loads, usually under 30-40% of their capacity, which is mainly cause wet stacking. Operating a diesel generator at low levels prevents the engine from reaching the heat needed for fuel to burn completely. This leads to unburned fuel and partially burnt hydrocarbons collecting in the exhaust. Together with the buildup of oil and soot, this creates the “wet chimney” look typical of wet stacking.
Extended idle
Extended idle speeds exacerbate low load issues because the engine is running below its designed capacity for long periods of time, hindering proper combustion and promoting wet stacking.
Oversized generators
If a diesel generator is sized larger than the typical load requirements, it means it is rarely running at its optimal load. This mismatch prevents the engine from reaching operating efficiency, resulting in incomplete combustion.
Frequent starts and stops
Short operating intervals do not allow the diesel engine enough time to reach and maintain optimal operating temperature, resulting in incomplete fuel combustion and increasing the risk of wet stacking.
Poor fuel quality
Low quality fuel can dramatically reduce combustion efficiency. Such fuels often burn incompletely, causing a buildup of unburned hydrocarbons in the generator exhaust system.
Injector or fuel system malfunction
Contaminated or faulty fuel injectors can cause poor spray patterns, as well as excessive wear on components such as valve guides. Inefficient fuel delivery can lead to incomplete combustion, which can cause wet stacking in diesel generators and damage engine components such as pistons and rings.
Low ambient temperature
Lower temperatures increase the likelihood of condensation in the exhaust, exacerbating the wet stacking effect. Cold conditions prevent diesel engines from reaching sufficient temperatures for adequate combustion.
Inadequate loading during scheduled maintenance test runs
Maintenance runs that do not adequately load diesel generators fail to test the full functionality of the generator, resulting in continuous low load conditions, which can lead to wet stacking.
Knowing these causes, we can simply judge by the following symptoms.
- Symptoms of wet stacking in diesel generators
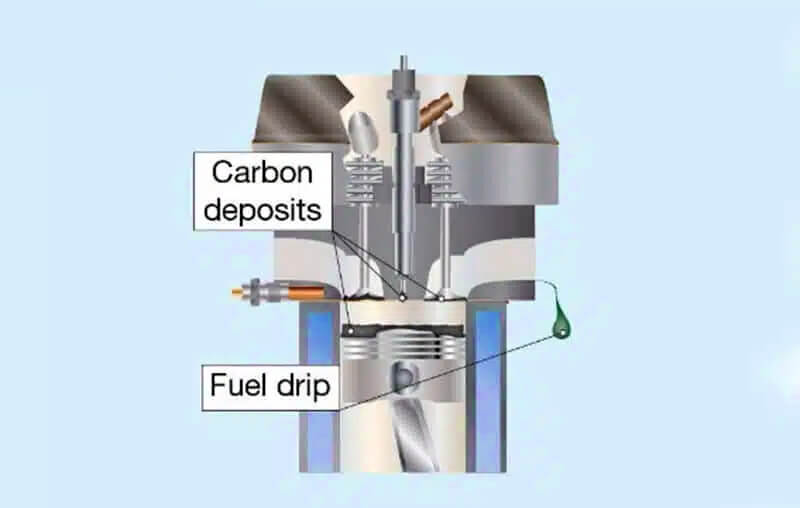
- Continuous emission of black smoke, which indicates incomplete combustion, and unburned fuel will be discharged from the exhaust pipe.
- Unburned fuel mixes with soot, condenses and drips black material from the exhaust pipe.
- Unburned fuel and carbon particles can build up, creating deposits in the exhaust system.
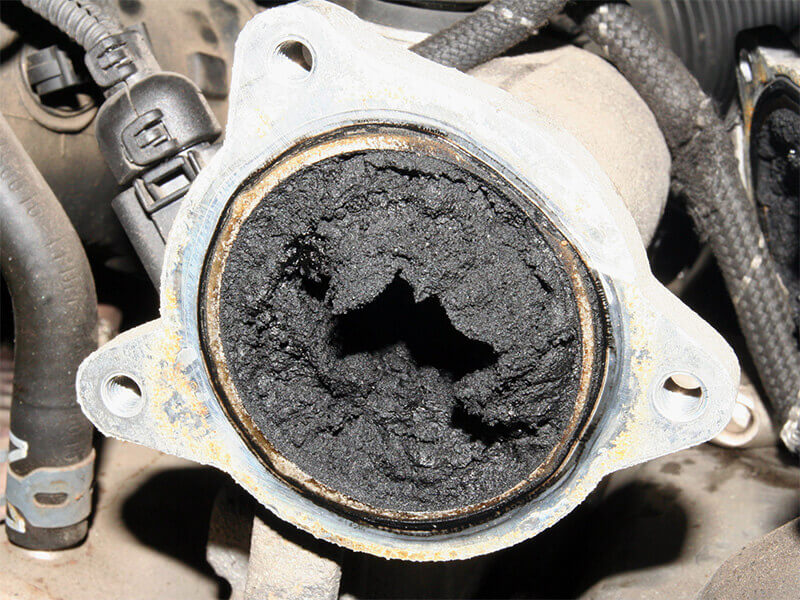

Effects of wet stacking in diesel generators
- Poor performance and shortened engine life: Incomplete combustion lowers efficiency, diminishes power and accelerates wear, thereby shortening the service life of diesel generators.
- Increased maintenance costs: Frequent cleaning and repairs are required to address soot and carbon deposits, increasing diesel generator maintenance costs.
- Carbon deposits in exhaust systems: Unburned or partially burned fuel and carbon deposits can clog exhaust pipe, reducing airflow and further affecting performance.
- Violations of emission regulations: Too much smoke and emissions from incomplete combustion in diesel generators, can lead to violations of environmental standards, potentially resulting in fines or operational limits.
By understanding above causes and their effects, operators can take sensible steps to mitigate wet stacking, and maintain diesel generator efficiency and life.
Preventing wet stacking in diesel generators
Proper generator sizing
It is critical to ensure that the capacity of diesel generator matches expected load. A properly sized diesel generator will operate efficiently and reduce the risk of wet stacking.
Regular load operation
Running your diesel generator at high load (75-100% of capacity) for several hours on a regular basis can help burn off accumulated deposits. This practice maintains optimal engine temperatures and promotes complete combustion.
Proper maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent wet stacking. This includes changing fuel filters, cleaning and testing fuel injectors, and inspecting the exhaust system for blockages or stacking.
Load bank testing
Utilizing a load bank to simulate real-world loads ensures your diesel generator is operating under optimal conditions, helping to prevent fuel build-up and maintain efficiency.
Using fuel additives
Fuel additives can boost combustion efficiency and lower the risk of incomplete burning. However, weigh the advantages and disadvantages, since some additives might impact diesel engine parts differently.
Latest diesel generator technology
Investing in a modern diesel generator with advanced combustion technology and emissions controls can inherently reduce the risk of wet stacking.
Solving an existing wet stack problem
- Early stages: Run your diesel generator at 75-100% load for several hours. This can help burn off small amounts of deposits, improving combustion and performance.
- Severe cases: If deposits are significant, hire a qualified technician. They can clean the exhaust system and any other affected areas, restore the efficiency of the diesel generator and prevent further problems.
By implementing these strategies, operators can effectively prevent wet stacking, ensure efficient operation and extend the service life of diesel generators. Regular attention and proper use are key to maintaining optimal performance of diesel generators.
In this article, BISON explores the basic ways to prevent wet stacking in diesel generators, select the appropriate generator size, conduct regular load operation, load testing, use fuel additives or adopt the latest diesel generator technology, upgrade to advanced models to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Taking these measures may prevent wet stacking in diesel engines. However, if the above methods are still not resolved.
In this case, contact a diesel generator service provider to inspect and repair your diesel generator.
contact us
related product categories
Get in touch to speak with our experts!






